Core CCTV System Components Explained
A CCTV system isn’t just about cameras - it’s a complete setup made of several working parts that come together to capture, transmit, record, and view video footage.
Understanding each component helps you choose the right system, troubleshoot issues, and design a setup that actually works for your space.
In this guide, we’ll break down the core components of a CCTV system and what each one does.
CCTV Cameras
The camera is where everything starts. It captures video of the area being monitored.
Different types of cameras such as
- dome cameras for discreet indoor coverage,
- bullet cameras for long-range outdoor views, and
- PTZ (Pan-Tilt-Zoom) cameras for dynamic monitoring
are chosen based on space size, lighting, and coverage needs.
Pro Tip: For wide coverage in a retail store, a 2.8mm fixed lens dome camera is often preferred to minimize blind spots.
Lenses
Lenses determine how much of a scene is captured and how detailed it appears.
- Fixed lenses (e.g., 2.8mm, 3.6mm) offer a set viewing angle.
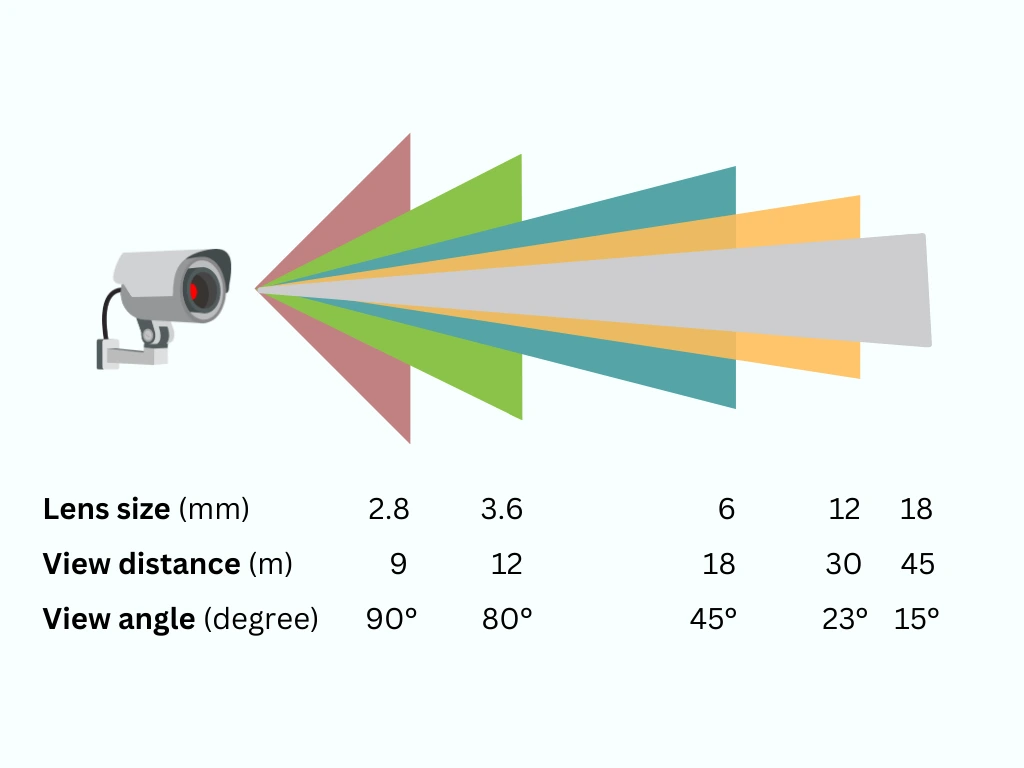
CCTV camera lenses displayed to show various viewing angles and distance coverage.
- Varifocal lenses (e.g., 2.8-12mm) allow manual or motorized zooming for flexible setups.
Example: A 2.8mm lens offers approximately a 90° field of view, ideal for small rooms or hallways, while a 12mm lens provides a tighter, more zoomed-in image for long corridors.
Cables or Wireless Transmitters
Video data needs a reliable way to travel from the camera to the monitor or recorder.
- Coaxial cables (e.g., RG59) are commonly used in analog systems and can carry video signals up to around 300 meters without a signal booster.
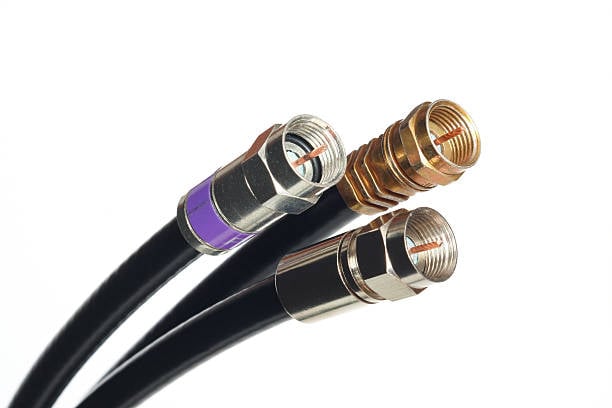

Coaxial cables for signal transmission
- Ethernet cables (e.g., Cat5e, Cat6) are standard for IP-based CCTV systems. They reliably support distances up to 100 meters between devices, following industry best practices for maintaining full data speed and video quality.
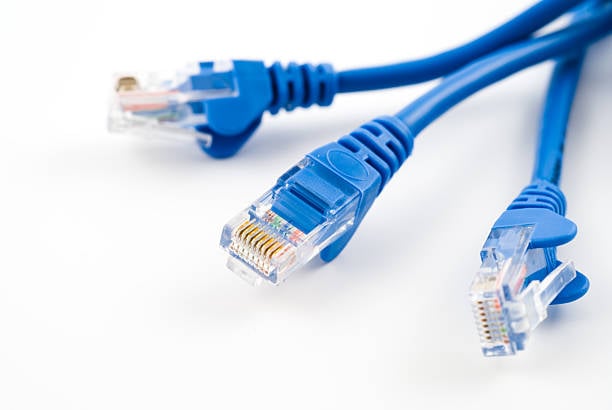

Network cables for signal transmission
While some systems offer wireless transmission (Wi-Fi or point-to-point), we do not recommend Wi-Fi for CCTV. Wireless setups often cause choppy video, signal interference, and lag, especially with high-resolution recordings.
Pro Tip: For best results, a wired connection is strongly recommended.
Learn more in how CCTV transmission methods work.
Video Recorder (DVR/NVR)
The recorder acts as the brain of the CCTV system.
- DVRs (Digital Video Recorders) handle analog camera inputs and often record in H.264 or H.265 compression.
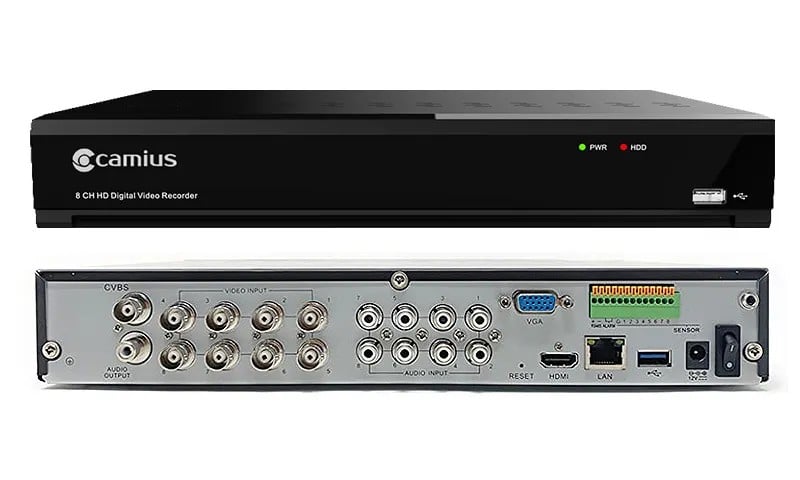

8-channel DVR showing front panel and rear coaxial ports for camera input.
- NVRs (Network Video Recorders) work with IP cameras and typically offer features like remote access, AI analytics, and higher resolution support (up to 4K).
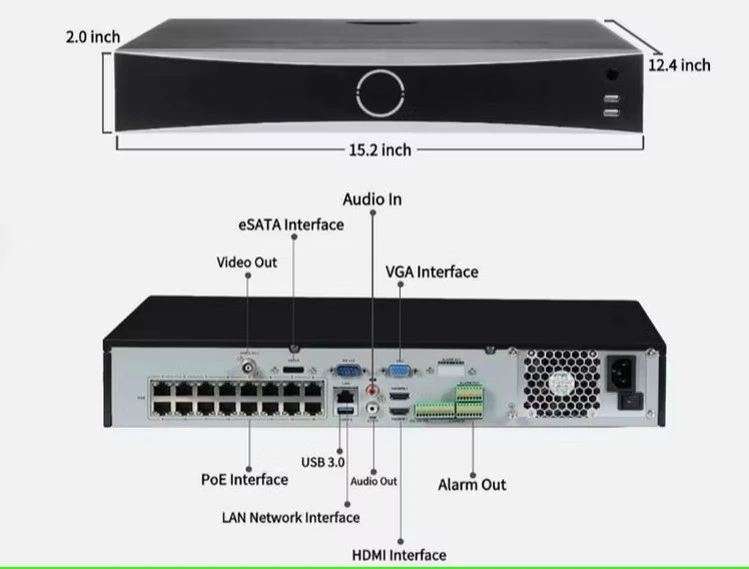
16-channel NVR showing front panel and 16 PoE ports for cameras.
Pro Tip: Always choose an NVR that supports ONVIF standards for better camera compatibility.
Get the details in CCTV video storage.
Monitor or Display
Monitors let you view live or recorded footage. They can range from small 19-inch screens for basic setups to large multi-view displays used in surveillance control rooms.
For a multi-camera system, a 1080p or higher resolution monitor is recommended to avoid image distortion when displaying multiple feeds at once.
Pro Tip: When using multiple monitors, a monitor arm or stand helps organize the workspace and allows flexible adjustment - essential for control rooms managing many live feeds.
Power Supply
Each component, especially the cameras and recorders - requires a reliable power source.
- Smaller setups may use individual 12V DC adapters (~500mA per camera).
- Larger installations typically rely on a centralized power box to distribute power cleanly across multiple cameras.
- Power over Ethernet (PoE) setups allow both data and power through a single Cat5e or Cat6 cable, simplifying installation.
More on this in CCTV power supply.
Control Interface
The control interface is how users interact with the system, through either software platforms or physical controllers.
- Popular software interfaces include Milestone XProtect, Hikvision iVMS-4200, and Dahua Smart PSS.
- Interfaces allow users to switch camera views, playback recordings, configure settings, and set up smart alerts.
You can read more in CCTV control interfaces.
Mounting Hardware and Enclosures
Cameras must be securely installed with proper mounting hardware suited to their environment.
- Outdoor cameras typically use IP66 or IP67-rated enclosures for weather protection.
- Junction boxes are often used to conceal and protect cabling, especially in vandal-prone or wet areas.
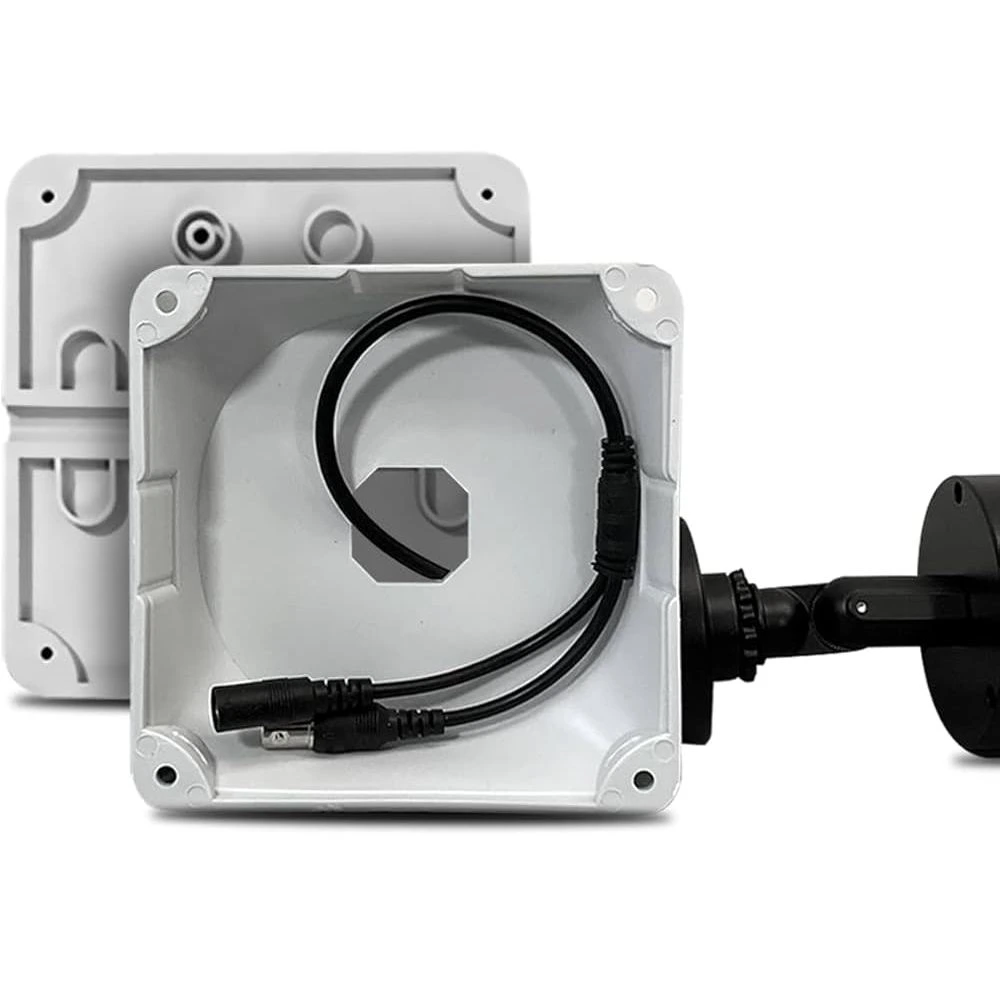

Junction box used in CCTV installations to protect and organize camera cables.
Pro Tip: For coastal or high-humidity areas, consider stainless steel housings to prevent corrosion.
Wrapping It Up
Each component plays a key role in how effective your CCTV system is. Whether you're planning a new setup or upgrading an old one, knowing how these parts work together gives you a big advantage.
Next up: Take a closer look at the different types of CCTV cameras and how they match different environments and needs.

